Editors-in-Chief Conference on Economics
经济学“主编面对面”会议
Editors-in-Chief Conference on Economics

• 顶级经济学期刊主编同步在线,学术权威共襄盛会
• Editors-in-Chief of top economics journal will attend, lecture and communicate in the conference online
• 顶级经济学期刊主编
• Editors-in-Chief of top economics journals
1. Tilman Börgers, Journal of Economic Theory
2. Toni Whited, Journal of Financial Economics
3. Nathanie Hendren, Journal of Public Economics
4. Andreas Lange, Journal of Environment Economics and Management
5. Stuart S. Rosenthal, Journal of Urban Economics
6. Giacomo Calzolari, International Journal of Industrial Organization
7. Daniela Puzzello, Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization
• 经济学主编面对面会议日程
• Agenda for Editors-in-Chief Conference on Economics
会议时间:
全体会议:6月20日(星期一),20:00-23:00(北京时间)
专题研讨会:6月21日—6月29日(除周末), 20:00-22:00(北京时间)
Time:
Plenary Session: 20:00-23:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00, Monday, 20 June ,2022)
Thematic Session: 20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00, weekdays, 21-29 June, 2022)
• 会议地点:Zoom会议
(会议号:814 3532 0639 / 会议链接:https://universityofleeds.zoom.us/j/81435320639)
Venue: Zoom Meeting
(Webinar ID: 814 3532 0639 / Webinar Link: https://universityofleeds.zoom.us/j/81435320639)
• 日程安排
• Daily Schedule
Plenary Session: Introduction to economic journals and writing & submission skills
全体会议:介绍各期刊特色及写作投稿经验
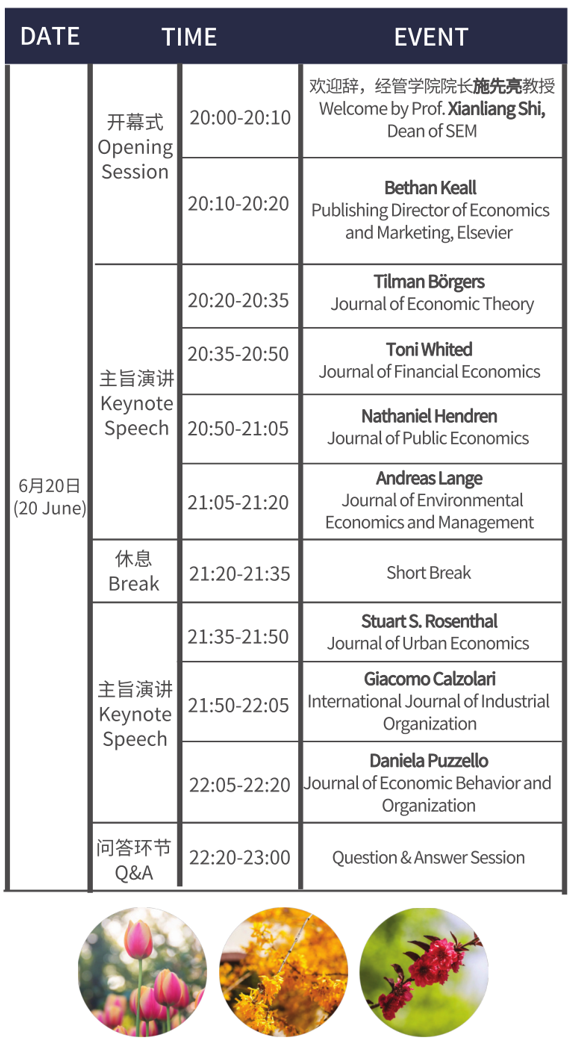
Thematic Session: Editors-in-Chief share the state-of-the-art research
专题讲座:顶级期刊主编分享最新的深度研究
Note:All the events include comments and Q&A
• 特邀嘉宾
• Special Invited Guest
Bethan Keall 思唯尔经济学期刊出版总监 | Bethan Keall, Publishing Director, Economics and Marketing, STM Journals, is responsible for Elsevier's Economics and Business journals. Bethan has spent 20 years working in various publishing roles, firstly with the Sales team and since 2009 within Journals at Elsevier. In her roles in both the Physical Sciences and Social Sciences journals units, she has launched innovative precursors to Sneak Peek at Cell and First Look and overseen OA launches together with using a books discount code for reviewers and initiating database linking in Earth Sciences. Her group currently manage more than 20 society-owned or affiliated journals. |
• 期刊主编
• Editors-in-Chief
Tilman Börgers Journal of Economic Theory | Tilman Börgers grew up in Germany, and obtained a PhD in economics from the London School of Economics. He has taught at the University of Basel and at University College London, and is currently the Samuel Zell Professor of the Economics of Risk at the University of Michigan. His research areas are game theory, the theory of mechanism design, and other topics in microeconomic theory. His research has been published in leading economics journals, such as Econometrica, the Review of Economic Studies, and the American Economic Review. He is the author of a textbook on the theory of mechanism design. He regularly teaches undergraduate and graduate courses in economic theory, and he has been chair or co-chair of the committees of 17 PhD students. He is currently the lead editor of the Journal of Economic Theory, having served on numerous editorial boards in the past. He is a former director of the Center for Economic Learning and Social Evolution at University College London. |
Toni Whited Journal of Financial Economics | Tilman Börgers grew up in Germany, and obtained a PhD in economics from the London School of Economics. He has taught at the University of Basel and at University College London, and is currently the Samuel Zell Professor of the Economics of Risk at the University of Michigan. His research areas are game theory, the theory of mechanism design, and other topics in microeconomic theory. His research has been published in leading economics journals, such as Econometrica, the Review of Economic Studies, and the American Economic Review. He is the author of a textbook on the theory of mechanism design. He regularly teaches undergraduate and graduate courses in economic theory, and he has been chair or co-chair of the committees of 17 PhD students. He is currently the lead editor of the Journal of Economic Theory, having served on numerous editorial boards in the past. He is a former director of the Center for Economic Learning and Social Evolution at University College London. |
Nathaniel Hendren Journal of Public Economics | Nathaniel Hendren is a Professor of Economics at Harvard University. He is a Founder and Co-Director of Policy Impacts, an organization dedicated to improving the quality of government decision-making and evidence-based policy-making. He is also a Founder and Co-Director of Opportunity Insights, which is dedicated to identifying barriers to economic opportunity and developing scalable solutions that will empower people throughout the United States to rise out of poverty and achieve better life outcomes. He has been awarded the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) in 2019 and a Sloan Fellowship in 2016. He is the lead co-editor of the Journal of Public Economics and Associate Editor at American Economic Review: Insights. |
Andreas Lange Journal of Environmental Economics and Management | Andreas Lange is Full Professor of Economics, esp. Public Economics at Universität Hamburg. Before, he had an appointment as Assistant Professor at the University of Maryland. He is Research Associate at the Centre for European Economic Research (ZEW) as well as Research Fellow at CESifo München and within the RWI Research Network. From 2016-2019 he was Visiting Professor at Gothenburg University. Andreas received his PhD from the Department of Economics, University of Heidelberg. He serves as Co-Editor-in-Chief for Journal of Environmental Economics and Management. His current research comprises work on the voluntary provision of public goods, on climate policy, and decisions under uncertainty. Methodologically, he combines theoretical and experimental studies. Andreas’ research has been published in leading economic journals like American Economic Review, Quarterly Journal of Economics or Journal of Public Economics. |
Stuart S. Rosenthal Journal of Urban Economics | Stuart S. Rosenthal is the Maxwell Advisory Board Professor of Economics at Syracuse University. He is also a Senior Research Associate in the university's Center for Policy Research. Professor Rosenthal serves on the editorial boards for a number of academic journals. He is a Fellow of the Homer Hoyt School of Advanced Studies in Real Estate and Urban Economics and a Fellow of the Regional Science Association International (RSAI). In 2013, Professor Rosenthal received the RSAI Walter Isard Award for Scholarly Achievement. In 2013-2015 he served as Vice President and then President of the American Real Estate and Urban Economics Association (AREUEA). He served on the Council of the Urban Economic Association (UEA), 2009-2015, and chair of the department of economics at Syracuse 2017-2021. Since 2007, Professor Rosenthal has been serving as one of the two Managing Editors of the Journal of Urban Economics. |
Giacomo Calzolari International Journal of Industrial Organization | Giacomo Calzolari is professor of economics at the European University Institute, fellow at Center for Economic Policy and Research, and member of the group of experts at DG-Competition of the European Commission. He has published in American Economic Review, Science, Rand Journal of Economics, Journal of Economic Theory, Review of Financial studies. He is main editor of the International Journal of Industrial Organization. His research interests include industrial organization, microeconomic theory, competition policy, artificial intelligence, economics of regulation and banking regulation and supervision. |
Daniela Puzzello Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization | Daniela Puzzello is a Professor of Economics at Indiana University. Professor Puzzello's research interests are in economic theory, experimental economics and monetary economics. Her research integrates theory and experiments to study social norms of exchange, welfare improving trading institutions, mispricing in asset markets and the impact of monetary policies on economic outcomes. Daniela's research has been published in several journals, including American Economic Review, Econometrica, Journal of Economic Theory, Economic Theory, European Economic Review, Games and Economic Behavior, International Economic Review, Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, Journal of Mathematical Economics and Journal of Monetary Economics. She is Co-Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, Associate Editor for Economic Theory and an Editor of B. E. Journal of Theoretical Economics. |
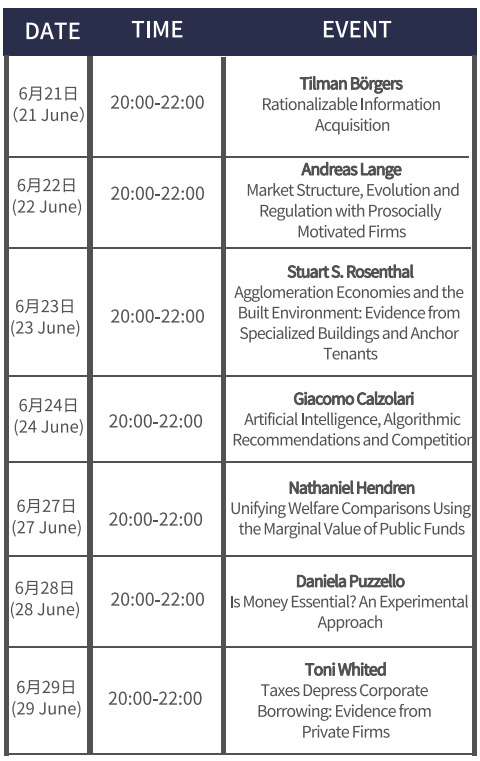
• 专题研讨会简介
• Thematic Session Introduction
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 21 June, 2022 |
Tilman Börgers Journal of Economic Theory | Rationalizable Information Acquisition Information sources may be of different quality. One formal concept of economic theory that captures the idea of information quality is the classic notion of "Blackwell dominance." A rational decision maker who chooses among information sources will never choose one such source if another source is available that Blackwell dominates the former. This is independent of the decision problem that the decision maker faces and for which the information is relevant. In this talk I shall address the reverse question: If an information source is not Blackwell dominated by any other available information source, is there a scenario in which it is rational for a decision maker to choose that information source? I shall show that the answer to this question is "yes," but that care needs to be taken with the precise formalization of the statement. In particular, we will encounter some ideas that are useful not only for the rational choice of information sources, but also for rational decision making in a variety of other contexts. The talk is based on joint work with Xienan Cheng.
点评人 李建培,教授,对外经济贸易大学 刘烁,助理教授,北京大学
Discussants Jianpei Li, Professor, University of International Business and Economics Shuo Liu, Assistant Professor, Peking University | ||
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 22 June, 2022 |
Andreas Lange Journal of Environmental Economics and Management | Market Structure, Evolution and Regulation with Prosocially Motivated Firms Social enterprises serve stakeholder interests beyond pure shareholder value. We construct a rich model to understand how social enterprises affect the structure, evolution, and regulation of markets where externalities are a component of product quality, e.g., environmentally-friendly and socially-responsible products. We solve for equilibrium configurations and identify a unique role for social enterprises: they can discover latent consumer preferences and spur product innovation. We further show how regulations (i.e., standards or prices on externalities) impact product characteristics, both directly and indirectly, by altering incentives for product differentiation. Our work offers unique insights on social enterprises and their multifaceted market impacts
点评人 张俊杰,副教授,杜克大学 李智,副教授,厦门大学
Discussants Junjie Zhang, Associate Professor, Duke Kunshan University Zhi Li, Associate Professor, Xiamen University | ||
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 23 June, 2022 |
Stuart S. Rosenthal Journal of Urban Economics | Agglomeration Economies and the Built Environment: Evidence from Specialized Buildings and Anchor Tenants This paper considers the effect of the built environment on commercial real estate markets and agglomeration economies. The paper shows that individual buildings are specialized beyond what random assignment of establishments would generate. The presence of an anchor tenant skews the composition of other tenants in the building towards the anchor's industry by 10 to 35%; an anchor tenant elsewhere on the same blockface has a much weaker effect, while an anchor across the street has little impact. These results are consistent with rapidly attenuating agglomeration economies. The pattern is especially strong in the retail sector, suggesting valuable within-building shopping externalities. Attenuation is also rapid in information-oriented office industries that rely on face-to-face interaction. Manufacturing is different in ways that suggest less reliance on in-person interaction between firms. Our findings suggest that building managers have potential to increase productivity by seeking complementary tenants.
点评人 李善军,教授,康奈尔大学 李敬,助理教授,新加坡管理大学
Discussants Shanjun Li, Professor, Cornell University. Jing Li, Assistant Professor, Singapore Management University | ||
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 24 June, 2022 |
Giacomo Calzolari International Journal of Industrial Organization | Artificial Intelligence, Algorithmic Recommendations and Competition We explore the impact of recommender systems (i.e., algorithms that use personal data to predict tastes and make recommendations to consumers) on market concentration and the intensity of competition. We model consumer preferences in a flexible way that allows for varying degrees of vertical and horizontal product differentiation. The analysis shows that recommender systems produce a significant increase in market concentration with respect to an individual search benchmark. We then analyze the causes and consequences of such an increase. We show that the increase in market concentration is not due to the "feedback loop" created by the endogeneity of the data, and that it is associated with an increase in the intensity of competition. We discuss the implications of these findings for competition policy.
点评人 周俊杰,教授,清华大学 张天乐,副教授,香港岭南大学
Discussants Junjie Zhou, Professor, Tsinghua University Tianle Zhang, Assoicate Professor, Lingnan University | ||
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 27 June, 2022 |
Nathaniel Hendren Journal of Public Economics | Unifying Welfare Comparisons using the Marginal Value of Public Funds We discuss how the marginal value of public funds (MVPF) can be used to conduct comparative welfare analyses of government policy changes. We illustrate the approach by studying 133 historical policy changes over the past half-century in the United States, focusing on policies in social insurance, education and job training, taxes and cash transfers, and in-kind transfers. Comparing MVPFs across policies provides a unified method of assessing their impact on social welfare. Our results suggest that direct investments in low-income children’s health and education have historically had the highest MVPFs, on average exceeding 5. Many such policies have paid for themselves as governments recouped the cost of their initial expenditures through additional taxes collected and reduced transfers. We find large MVPFs for education and health policies amongst children of all ages, rather than observing diminishing marginal returns throughout childhood. We find smaller MVPFs for policies targeting adults, generally between 0.5 and 2. Expenditures on adults have exceeded this MVPF range in particular if they induced large spillovers on children.
点评人 傅十和,教授,厦门大学 施新政,副教授,清华大学
Discussants Shihe Fu, Professor, Xiamen University Xinzheng Shi, Associate Professor, Tsinghua University | ||
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 28 June, 2022 |
Daniela Puzzello Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization | Is Money Essential? An Experimental Approach Money is called essential when (welfare) superior outcomes are incentive feasible with money than without it. We study the essentiality of monetary exchange experimentally, using finite horizon models, which suit our purposes better than the usual infinite horizon models. Following mechanism design methods, we also study the effects of strategy recommendations, both when they are incentive compatible and when they are not. We find the use of money is significantly higher when it is essential, and recommendations help only when incentive compatible. Sometimes money is accepted when it is not a best response, and we investigate why.
点评人 刘潇,副教授,清华大学 包特,副教授,新加坡南洋理工大学
Discussants Tracy Xiao Liu, Associate Professor, Tsinghua University Te Bao, Associate Professor, Nanyang Technological University | ||
20:00-22:00 (UTC/GMT+8:00), 29 June, 2022 |
Toni Whited Journal of Financial Economics | Taxes Depress Corporate Borrowing: Evidence from Private Firms We re-examine the relation between taxes and corporate leverage, using variation in state corporate income tax rates. In contrast with prior research, we document that corporate leverage increases following tax cuts for both privately held and publicly listed firms. We use an estimated dynamic equilibrium model to show that tax cuts result in lower default spreads and more distant default thresholds. These effects outweigh the loss of benefits from the interest tax deduction and lead to higher leverage, especially for privately held firms. Overall, debt tax shields appear to be a secondary capital structure consideration.
点评人 刘晓蕾,博雅特聘教授,北京大学 戴芸,副教授,中山大学
Discussants Laura Xiaolei Liu, Boya Distinguished Professor, Peking University Yun Dai, Associate Professor, Sun Yat-sen University | ||

















